
According to the EPA, commercial buildings and industrial facilities are responsible for 45% of US greenhouse gas emissions and generate about 50% of US carbon dioxide emissions. A staggering 30% of the energy consumed in commercial and industrial buildings is wasted because of poor power quality.
Some of the waste up to 10% can be reduced by implementing a power factor correction. Power factor correction is a technique you can implement to make your use of electricity more efficient saving money and reducing heat and transmission loss on the environment.
What is Power Factor?
Power factor (PF) is a term used to describe energy efficiency and is usually expressed as a percentage. The lower the percentage, the less efficient the use of power. It can be used to refer to a piece of equipment or an entire system in a building. It represents the ratio between how effectively your electrical equipment converts electric current (supplied by your power utility) into useful power output. Mathematically expressed it’s PF = kW/KVA or Power Factor = Active Power (kW) to the Apparent Power (KVA).
It’s not an easy concept to understand. The best way is by using the beer example. You buy a glass of beer, and when poured, you get both beer and foam. We get good value for our money when we get more beer than foam. Not so much if we get more foam than beer. More foam is not a good value.
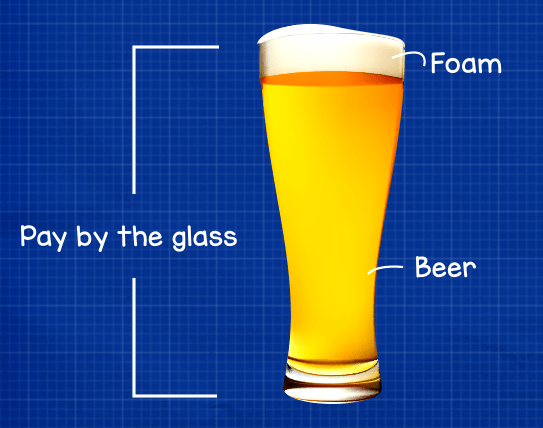
The same applies to power. The beer is our Active power or KW. The part that we need and for what we want to pay. The foam is our Apparent power or KVA; it’s rather useless. We end up paying for it, but we’d like to get as little as possible of it. So if your equipment or power system is demanding more power than it is using, you pay more for your electricity than required.
What is Power Factor Correction?
Power factor correction is the process of improving low power factor on a piece of equipment or a building’s power system by installing power factor correction capacitors. Installing capacitors increases the ratio of active power (beer) over apparent power (foam).
Power Factor Correction Benefits
Understanding power factor is crucial because it saves a company money while decreasing their carbon footprint. When equipment or a power system has a low power factor, it is demanding significantly more power than it is using. This demand results in higher electricity charges and increases the amount of energy required from the power grid.
Other benefits of power factor correction:
- Saves energy.
Energy loss can be reduced by up to 30% depending on the level of capacitor compensation. - Increases energy efficiency.
By optimizing the power factor, your power quality increases improving performance and reducing unplanned outages which lessen potential damage to your electrical network. - Reduces equipment costs.
An efficient power factor allows you to use smaller transformers, switchgear, and cables which improves the reliability and lifespan of the equipment. - Reduces carbon emissions.
Eliminating energy waste and overall consumption reduces heat and transmission losses on equipment and systems, which reduces your carbon footprint.